Are you experiencing discomfort and itching in your intimate area? Are you aware of pH and Yeast infection?
If so, it may be due to a vaginal pH yeast infection.
This common condition occurs when the natural balance of bacteria in your vagina is disrupted, allowing yeast to overgrow and cause irritation.
In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for vaginal pH yeast infections, helping you understand how to alleviate the discomfort and prevent future occurrences.
So, let’s dive into this topic and find the relief you’ve been seeking.
Table of Contents
pH and Yeast infection: Vaginal Causes, Symptom, & Treatment
Understanding Vaginal pH and Yeast Infections
What is Vaginal pH?
Vaginal pH refers to the acidity or alkalinity of the vaginal environment.
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with pH 7 being considered neutral.
In a healthy vagina, the pH level is slightly acidic, typically ranging from 3.8 to 4.5.
This mildly acidic pH helps maintain a balanced and healthy vaginal ecosystem by discouraging the growth of harmful bacteria and fungi.
What is a Yeast Infection?
A yeast infection, also known as vulvovaginal candidiasis, is a common type of vaginal infection caused by the overgrowth of a fungus called Candida.
The most common type of Candida responsible for yeast infections is Candida albicans.
Yeast infections can cause uncomfortable symptoms, such as itching, burning, and abnormal vaginal discharge.
The Relationship Between Vaginal pH and Yeast Infections
pH, or potential of hydrogen, is a measurement used to determine how acidic or alkaline a substance is.
In the case of yeast infections, pH plays a significant role.
The vagina naturally maintains an acidic environment with a pH level between 3.8 and 4.5.
This acidity helps to keep harmful bacteria and fungi, like Candida, in check.
When the vaginal pH becomes imbalanced and shifts towards being less acidic or more alkaline, it creates an environment that is more favorable for the growth of Candida fungus.
Consequently, a higher vaginal pH can increase the risk of developing a yeast infection.
Understanding the factors that can disrupt the vaginal pH balance is essential in preventing and managing yeast infections.
Effects of yeast infection on vaginal pH
A yeast infection can significantly impact the vaginal pH balance.
The elevated pH level that occurs during a yeast infection creates an environment that promotes the growth of yeast and inhibits the growth of beneficial bacteria.
This disruption in pH can lead to an imbalance in the vaginal microbiome, making it easier for recurrent infections to occur.
Restoring the normal pH balance is essential for resolving and preventing further yeast infections.
Can pH be used to diagnose a yeast infection?
While changes in pH can be an indicator of a yeast infection, it is not a definitive diagnostic tool.
Other factors, such as symptoms and microscopic examination, are typically used to confirm a yeast infection.
pH testing can be a helpful tool for self-diagnosis, but it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Can A pH Test Tell You If You Have A Yeast Infection?
Using pH tests for self-diagnosis
pH tests can be helpful in determining if you have a yeast infection, especially when used in conjunction with other symptoms.
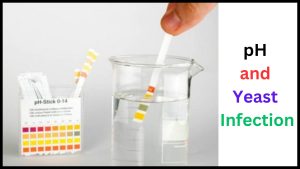
pH test strips, specifically designed for vaginal use, can be purchased over-the-counter.
By following the instructions provided, you can measure the pH level of your vagina and note any changes from the normal range.
However, it is important to remember that pH tests should not be the sole method of diagnosis.
Limitations of pH tests
While pH tests can provide some insight into the vaginal environment, there are limitations to their reliability in diagnosing a yeast infection.
Other conditions, such as bacterial vaginosis or sexually transmitted infections, can also cause changes in pH levels.
Therefore, it is vital to consider other symptoms and seek medical advice for a comprehensive evaluation.
How Can I Check My pH Balance?
Methods to check pH levels
There are several methods available to check your vaginal pH balance.
One of the most common methods is to use pH test strips designed for vaginal use.
These strips can be easily obtained over-the-counter at pharmacies or online.
Another option is to visit a healthcare professional who can perform a pH test during a routine examination.
Vaginal pH test strips
Vaginal pH test strips are a convenient and affordable option for checking your pH balance at home.
These strips are typically made of litmus paper and change color according to the pH level of the vaginal secretions.
By comparing the color of the strip to a provided color chart, you can determine the approximate pH level of your vagina.
pH level indicators at home
Some at-home pH testing kits may include a pH level indicator solution or gel.
These kits typically involve collecting a small sample of vaginal discharge and mixing it with the pH indicator solution.
The resulting color change can then be compared to a color chart to determine the vaginal pH level.
Importance of regular pH monitoring
Regular monitoring of your vaginal pH balance can help you understand your body’s natural fluctuations and detect any potential changes or imbalances.
By keeping track of your pH levels, you can take proactive measures to maintain a healthy vaginal environment and prevent issues such as yeast infections.
If you notice any significant changes or persistent symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
How Do You Know If Your pH Balance Is Good Female?
Indications of a balanced pH
A balanced pH in the female genital area is reflected by the absence of symptoms such as itching, burning, or abnormal discharge.
It is also associated with a healthy and normal vaginal odor.
When the pH is balanced, it indicates that the natural protective barrier of the vagina is functioning optimally and preventing the overgrowth of harmful microorganisms.
Normal vaginal pH range
The normal vaginal pH range falls between 3.8 and 4.5, which is slightly acidic.
Staying within this range is crucial for maintaining a healthy vaginal environment.
Fluctuations in pH levels may occur throughout the menstrual cycle, but as long as the pH remains within the normal range, it is generally considered to be a good balance.
Signs of pH imbalance
Signs of a pH imbalance in the female genital area may include itching, burning, abnormal discharge, and an unusual odor.
These symptoms can indicate the presence of an infection or an imbalance in the vaginal microbiome.
If you notice any of these signs, it is important to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What Are The Symptoms Of A pH Imbalance?

Physical symptoms of pH imbalance
A pH imbalance in the vagina can manifest in various physical symptoms.
These symptoms may include itching, redness, swelling, and discomfort.
They can range in severity from mild to severe and may fluctuate throughout the menstrual cycle.
If left untreated, a pH imbalance can lead to recurrent infections and chronic discomfort.
Common signs of vaginal pH imbalance
Common signs of a vaginal pH imbalance include changes in vaginal discharge, such as an increase in volume, change in color or consistency, and a strong or unpleasant odor.
It is important to note that these symptoms can be caused by various factors, so it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Other related symptoms
In addition to the physical symptoms, a pH imbalance in the vagina can also cause emotional and psychological distress.
Discomfort and embarrassment associated with these symptoms can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
Seeking timely medical advice and appropriate treatment is essential for resolving the symptoms and restoring a healthy vaginal pH balance.
What Pill Is Good For Yeast Infection?
Medication options for yeast infection
Yeast infections can be treated with several types of medication.
Over-the-counter antifungal creams, suppositories, or tablets are commonly used for mild to moderate infections.
Prescription-strength antifungal medications may be recommended for severe or recurring infections.
Depending on the severity of the infection, your healthcare professional will determine the most appropriate treatment method.
Antifungal pills for treating yeast infections
Antifungal pills, also known as oral antifungal medications, are a systemic treatment option for yeast infections.
These medications work by targeting the overgrowth of Candida throughout the body, including the vaginal area.
Commonly prescribed oral antifungal medications include fluconazole (Diflucan) and itraconazole (Sporanox).
These pills are typically taken orally as a single dose or as a course of treatment.
Effectiveness and considerations
Antifungal pills are generally effective in treating yeast infections, particularly those that are severe or recurrent.
However, it is important to note that oral antifungal medications may come with potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
It is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits with your healthcare professional before starting any medication.
Can Flagyl Treat A Yeast Infection?
Understanding Flagyl (Metronidazole)
Flagyl, also known by its generic name metronidazole, is an antibiotic medication commonly used to treat certain types of bacterial and parasitic infections.
While Flagyl is not typically prescribed as a first-line treatment for yeast infections, it may be used in certain cases where a secondary infection is present.
Effectiveness of Flagyl for Yeast Infections
Flagyl is not an antifungal medication and does not directly target the Candida fungus responsible for yeast infections.
Therefore, it may not be as effective in treating a yeast infection as antifungal medications specifically designed for that purpose.
However, if a secondary bacterial infection is present alongside the yeast infection, Flagyl may be prescribed to address both infections simultaneously.
Precautions and potential side effects
As with any medication, Flagyl comes with precautions and potential side effects that need to be considered.
Common side effects may include nausea, stomach cramps, and a metallic taste in the mouth.
It is important to discuss any pre-existing medical conditions or other medications you are taking with your healthcare professional before starting Flagyl or any other medication.
What Home Remedy Can I Use To Stop Yeast Infection?

Natural remedies for yeast infections
There are several home remedies that may help alleviate the symptoms of a yeast infection.
One commonly suggested remedy is the use of probiotics, either in supplement form or via yogurt containing live cultures.
Probiotics can help restore the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina.
Other natural remedies include tea tree oil, garlic, and coconut oil, which have potential antifungal properties.
Home remedies for relieving symptoms
To relieve the symptoms of a yeast infection, you can try taking warm sitz baths or applying cool compresses to the affected area.
Avoiding tight-fitting clothing and using unscented hygiene products can also help prevent further irritation.
However, it is important to note that home remedies may provide temporary relief, but they may not address the underlying cause of the infection.
If symptoms persist or worsen, it is advisable to seek medical advice.
Preventive measures to maintain healthy pH
Maintaining a healthy vaginal pH balance is crucial for preventing yeast infections.
To prevent recurring infections, you can take certain preventive measures.
These include avoiding the use of harsh soaps, douching, and heavily scented hygiene products.
Wearing breathable cotton underwear, practicing good hygiene, and managing other underlying conditions such as diabetes can also help maintain a healthy vaginal pH balance.
What Confirms A Yeast Infection?

Professional confirmation of yeast infections
While self-diagnosis based on symptoms and pH tests can provide some insight, it is important to seek confirmation from a healthcare professional.
They are better equipped to accurately diagnose a yeast infection and rule out other possible causes of your symptoms.
Medical examination and testing
A healthcare professional will conduct a thorough examination to assess the symptoms and signs of a yeast infection.
They may perform a pelvic examination or collect a sample of vaginal discharge to examine it under a microscope.
This examination and testing will help confirm the presence of yeast and rule out potential underlying conditions.
Diagnostic methods and accuracy
In addition to visual examination and microscopic evaluation, healthcare professionals may also perform culture tests to accurately diagnose a yeast infection.
These tests involve growing Candida in a laboratory setting to determine the specific type and sensitivity to different antifungal medications.
This information is instrumental in prescribing the most effective treatment plan for the specific strain of Candida causing the infection.
In conclusion, understanding the role of pH in yeast infections is crucial for effectively managing and preventing these common infections.
While changes in pH can indicate the presence of a yeast infection, they are not a definitive diagnostic tool.
Self-diagnosis based on symptoms and pH tests should always be confirmed by a healthcare professional for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
Regular monitoring of vaginal pH balance, along with maintaining proper hygiene and seeking timely medical advice, can help prevent recurring yeast infections and ensure overall vaginal health.

Causes Of Vaginal pH Imbalance
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause, can disrupt the delicate balance of the vaginal pH.
These fluctuations in hormone levels can alter the vaginal environment, making it more susceptible to yeast overgrowth.
Poor Hygiene
Poor hygiene practices, such as not cleaning the genital area thoroughly or using harsh soaps and perfumed products, can upset the natural pH balance of the vagina.
It is important to maintain good hygiene by gently washing the external genital area with mild, unscented soap and water.
Medications
Certain medications, such as antibiotics and corticosteroids, can disrupt the vaginal pH balance by killing off the beneficial bacteria that help keep yeast in check.
This can lead to an overgrowth of yeast and the development of a yeast infection.
If you are taking antibiotics or other medications, it is important to discuss with your healthcare provider about ways to minimize the risk of yeast infections.
Sexual Activity
Frequent or intense sexual activity can disrupt the vaginal pH and increase the risk of developing a yeast infection.
This is because sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria and other substances into the vagina, potentially altering its natural pH balance.
It is advisable to maintain good hygiene practices and urinate after sexual intercourse to help flush out any potential irritants or bacteria.
Diet and Lifestyle Factors
Certain dietary and lifestyle factors can influence the vaginal pH.
For example, a diet high in sugar and refined carbohydrates can contribute to an overgrowth of yeast.
Additionally, wearing tight-fitting, non-breathable underwear or using feminine hygiene products that contain irritants can disrupt the vaginal pH balance.
Medical Conditions
Certain underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and hormonal disorders, can increase the risk of developing recurrent yeast infections.
These conditions affect the body’s immunity and can create an environment that promotes the growth of yeast.
It is important for individuals with these conditions to work closely with their healthcare provider to manage their vaginal health effectively.
Signs and Symptoms of Yeast Infections

Itching and Irritation
One of the most common symptoms of a yeast infection is intense itching in the vaginal area.
The itching can be persistent and may worsen at night.
Scratching the area can further irritate the skin and lead to redness and inflammation.
Burning and Soreness
Yeast infections can cause a burning sensation in the genital area, especially during urination or sexual intercourse.
The burning sensation is often accompanied by soreness and discomfort, making it uncomfortable for individuals affected by the infection.
Abnormal Discharge
An abnormal vaginal discharge is another characteristic symptom of a yeast infection.
The discharge is typically thick and white, resembling cottage cheese.
It may also have a yeasty odor.
However, it is important to note that not all vaginal discharge is indicative of a yeast infection, as other types of infections can cause similar symptoms.
Painful Urination
Yeast infections can cause pain and discomfort during urination.
The acidic urine can irritate the inflamed vaginal tissues, leading to a stinging or burning sensation.
This symptom can be especially bothersome and may require prompt attention.
Painful Intercourse
Engaging in sexual intercourse can be painful and uncomfortable for individuals with yeast infections.
The inflamed vaginal tissues can become more sensitive, leading to pain and discomfort during penetration.
It is important to address this symptom and seek appropriate treatment to relieve the discomfort and prevent further complications.
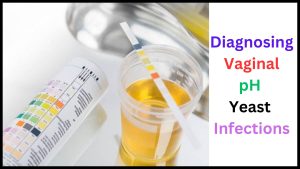
Diagnosing Vaginal pH Yeast Infections
Physical Examination
During a physical examination, a healthcare provider may inspect the genital area for any signs of infection.
They may look for redness, swelling, or other visible symptoms indicative of a yeast infection.
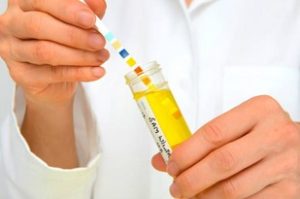
Vaginal pH Testing
Measuring the vaginal pH level can help confirm the presence of a yeast infection.
A healthcare provider may collect a sample of vaginal fluid using a swab and test the pH using specialized paper strips or a pH meter.
An elevated vaginal pH (greater than 4.5) can indicate a yeast infection.
Microscopic Examination
A microscopic examination of the vaginal fluid can be performed to identify the presence of yeast cells.
A healthcare provider may examine the vaginal fluid under a microscope to look for the characteristic yeast cells or hyphae.
This examination can provide a definitive diagnosis of a yeast infection.
Cultures and Tests for Specific Organisms
In some cases, a healthcare provider may order a culture or other specialized tests to identify the specific yeast species causing the infection.
This information can help guide treatment decisions, especially in cases of recurrent or severe yeast infections.
Preventing Vaginal pH Yeast Infections

Practice Good Hygiene
Maintaining good hygiene is essential in preventing vaginal pH imbalances and yeast infections.
This includes gentle cleaning of the external genital area with mild, unscented soap and water.
It is important to avoid using harsh soaps, douches, or other feminine hygiene products that can disrupt the natural pH balance.
Maintain a Healthy Diet
A healthy and balanced diet can contribute to overall vaginal health and prevent yeast infections.
It is advisable to limit the consumption of sugary and refined carbohydrate-rich foods, as these can promote yeast overgrowth.
Instead, focus on incorporating nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
Avoid Douching and Irritants
Douching, or the practice of cleansing the vagina with water or other solutions, can disrupt the vaginal pH balance and increase the risk of yeast infections.
It is important to avoid douching and also be cautious of using irritants, such as scented tampons, pads, or bubble baths, that can also upset the vaginal ecosystem.
Wear Breathable Underwear
Choosing breathable underwear made of cotton or other natural fibers can help maintain a healthy vaginal environment.
Breathable fabrics allow for air circulation, preventing moisture buildup and creating an unfavorable environment for yeast overgrowth.
It is best to avoid tight-fitting underwear or synthetic materials that can trap heat and moisture.
Practice Safe Sex
Practicing safe sex, including the use of condoms, can help reduce the risk of developing yeast infections.
Condoms can help prevent the introduction of harmful bacteria or fungi into the vagina, maintaining the natural pH balance.
It is important to follow safe sex practices and communicate openly with sexual partners about any signs or symptoms of infection.
Manage Stress Levels
High levels of stress can weaken the immune system and disrupt the vaginal pH balance, making individuals more susceptible to yeast infections.
Engaging in stress management techniques, such as regular exercise, relaxation exercises, and seeking support from loved ones, can help maintain overall health, including vaginal health.
Treating Vaginal pH Yeast Infections

Over-the-Counter Antifungal Medications
Over-the-counter antifungal medications, such as creams, suppositories, or tablets, are often the first line of treatment for mild yeast infections.
These medications contain antifungal agents, such as clotrimazole or miconazole, which help kill the yeast and relieve symptoms.
It is important to follow the instructions and complete the recommended course of treatment.
Prescription Medications
In cases of severe or recurrent yeast infections, a healthcare provider may prescribe stronger antifungal medications.
Prescription-strength creams, ointments, or oral medications may be necessary to effectively treat the infection.
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment option.
Home Remedies
Some individuals may find relief from mild yeast infections by using home remedies.
These include applying plain, unsweetened yogurt to the affected area or using diluted tea tree oil.
However, it is important to note that home remedies may not be as effective as medical treatments, and it is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before trying any home remedies.
Probiotics
Probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that help maintain a healthy balance of microorganisms in the body, may be used as a complementary treatment for yeast infections.
Also, Probiotics can help restore the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina and inhibit the growth of yeast.
They can be taken orally or used as vaginal suppositories.
Natural Remedies
Certain natural remedies, such as garlic, boric acid, or oregano oil, have been suggested as alternative treatments for yeast infections.
However, it is important to exercise caution when using natural remedies, as they may not be well-studied or regulated.
It is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before using any natural remedies for yeast infections.
When to Seek Medical Advice

Recurrent Infections
If you experience recurrent yeast infections, it is important to seek medical advice.
Recurrent infections may indicate an underlying health condition or other factors that need to be addressed.
A healthcare provider can help determine the cause of recurrent infections and develop an individualized treatment plan.
Severe Symptoms
If you experience severe symptoms, such as intense itching, pain, or persistent discomfort, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider.
Severe symptoms may require stronger medications or additional medical interventions to effectively treat the infection.
Pregnancy
Pregnant individuals who suspect they have a yeast infection should seek medical advice before using any medications.
Some antifungal medications may not be safe for use during pregnancy, and it is important to consult with a healthcare provider who can recommend appropriate treatment options.
Underlying Health Conditions
If you have underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or HIV/AIDS, it is important to work closely with your healthcare provider to manage your vaginal health effectively.
These conditions can increase the risk of developing recurrent yeast infections and may require additional considerations in treatment and prevention strategies.

Complications of Vaginal pH Yeast Infections
Chronic Yeast Infections
If left untreated or inadequately treated, yeast infections can become chronic or recurrent.
Chronic yeast infections can cause significant discomfort and may require more aggressive treatment strategies.
It is important to seek medical advice if you suspect a chronic yeast infection.
Vaginal Tears and Damaged Tissues
The itching, inflammation, and scratching associated with yeast infections can sometimes lead to vaginal tears and damage to the delicate tissues.
These tears can increase the risk of secondary infections and may prolong the healing process.
It is important to address yeast infections promptly to minimize the risk of complications.
Spread of Infection to Other Body Parts
In rare cases, untreated yeast infections can spread to other parts of the body, leading to more serious infections.
Candida overgrowth can affect areas such as the mouth, throat, and bloodstream, causing systemic candidiasis.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms beyond the vaginal area or if your symptoms worsen despite treatment.
Myths and Misconceptions about Vaginal pH and Yeast Infections

Only Women Get Yeast Infections
While yeast infections are more common in women, men can also develop yeast infections, especially in the groin area.
Male yeast infections can cause symptoms such as itching, redness, and soreness.
It is important to recognize that yeast infections can affect individuals of any gender.
Yogurt Cure for Yeast Infections
Although yogurt contains probiotics that can help restore the natural balance of bacteria in the body, it is not a cure for yeast infections.
While some individuals may find temporary relief from symptoms by applying yogurt topically, it is not a substitute for medical treatments.
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
Vaginal pH Can Be Controlled by Diet Alone
While diet can influence overall vaginal health, maintaining the optimal vaginal pH balance requires more than just dietary modifications.
Hormonal changes, medications, hygiene practices, and other factors can also affect the vaginal pH.
It is important to adopt a holistic approach to vaginal health, including a balanced diet, good hygiene practices, and other preventive measures discussed earlier.
Conclusion
Understanding the significance of vaginal pH and yeast infections is essential for maintaining good vaginal health.
By recognizing the factors that can disrupt the vaginal pH balance and practicing preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of developing yeast infections.
It is important to seek medical advice when necessary and to address recurrent or severe infections promptly to avoid complications.
By maintaining a balanced vaginal pH, individuals can enjoy optimal vaginal health and overall well-being.



