
Today, we will explore the topic of irritation of the labia minora, a common concern that affects many women.
Whether you are experiencing discomfort or simply seeking to educate yourself on this issue, we will provide you with valuable information to understand the causes, symptoms, and potential remedies for irritation of the labia minora.
By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of this condition and how to alleviate any discomfort it may cause.
So, let’s delve into the world of labia minora irritation and find the answers you are looking for!
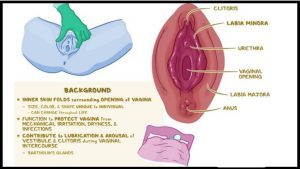
Table of Contents
Causes of Irritation
1. Allergic reactions
2. Chemical irritants
3. Fungal infections
4. Bacterial infections
5. Sexually transmitted infections
6. Poor hygiene
7. Tight clothing
8. Friction and rubbing
9. Menopause
10. Hormonal imbalances
1. Allergic reactions
Allergic reactions can cause irritation of the labia minora.
This can be triggered by various substances, such as certain fabrics, harsh soaps or detergents, or chemical additives in personal care products.
When you come into contact with an allergen, your immune system may overreact and produce symptoms such as itching, redness, and swelling.
Identifying and avoiding the specific allergen can help prevent further irritation.
2. Chemical irritants
Exposure to chemical irritants can also lead to irritation of the labia minora.
These irritants can be found in various products we use daily, such as scented soaps, perfumes, vaginal sprays, or certain types of lubricants.
The chemicals in these products can disrupt the natural balance of the vaginal area and cause discomfort or inflammation.
It is important to read labels and choose products that are gentle and free from irritants.
3. Fungal infections
Fungal infections, such as yeast infections, can cause irritation of the labia minora.
Yeast is a type of fungus that naturally occurs in the vaginal area, but an overgrowth can occur due to factors like poor hygiene, antibiotics, hormonal changes, or a weakened immune system.
Symptoms of a fungal infection may include itching, burning, and abnormal vaginal discharge.
Antifungal creams or medications are often used to treat these infections.
4. Bacterial infections
Bacterial infections, such as bacterial vaginosis, can also lead to labia irritation.
Also, bacterial vaginosis occurs when there is an imbalance in the natural bacterial flora of the vagina, allowing harmful bacteria to overgrow.
This can cause symptoms such as itching, redness, a foul-smelling discharge, and discomfort.
Antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare professional are often used to treat bacterial vaginosis.
5. Sexually transmitted infections
Several sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can cause irritation of the labia minora.
Examples include herpes, chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, and human papillomavirus (HPV).
These infections can be contracted through sexual contact with an infected partner.
Symptoms may vary depending on the specific infection but can include itching, redness, sores, ulcers, discharge, and pain during intercourse or urination.
It is important to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment if you suspect you may have an STI.
6. Poor hygiene
Poor hygiene practices can contribute to labial irritation.
Failing to clean the genital area properly or using harsh soaps or excessive douching can disrupt the natural balance of the vaginal area, leading to discomfort or inflammation.
Practicing good hygiene, including gentle cleaning with mild soaps and water, can help prevent irritation.
7. Tight clothing
Wearing tight or non-breathable clothing can trap moisture and heat, creating an environment that promotes the growth of bacteria or fungi.
This can lead to irritation of the labia minora.
Opting for loose, breathable underwear and clothing made from natural fibers can help reduce irritation caused by tight clothing.
8. Friction and rubbing
Friction and rubbing of the labia minora can cause irritation, especially during activities such as vigorous sexual activity or sports.
This can lead to symptoms such as redness, soreness, and discomfort.
Using lubrication during intercourse and wearing appropriate protective clothing during physical activities can help minimize friction and reduce irritation.
9. Menopause
During menopause, hormonal changes in the body can cause thinning and drying of the vaginal tissues, leading to labial irritation.
Estrogen levels decrease, which can result in a lack of lubrication and increased sensitivity.
Hormone therapy prescribed by a healthcare professional can help alleviate these symptoms and reduce irritation.
10. Hormonal imbalances
Hormonal imbalances can also contribute to labial irritation.
Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as those that occur during the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, or certain medical conditions, can affect the health of the vaginal tissues.
This can lead to symptoms such as itching, redness, or dryness.
Addressing the underlying hormonal imbalance through medical treatments or lifestyle changes may help improve labia irritation symptoms.

Symptoms of Irritation
1. Itching
2. Burning sensation
3. Redness and swelling
4. Dryness and flaking
5. Pain or discomfort
6. Abnormal vaginal discharge
7. Painful urination
8. Painful intercourse
9. Soreness
10. Tenderness
1. Itching
One of the most common symptoms of labial irritation is itching.
Itching can be mild to severe and can be accompanied by a strong urge to scratch the affected area.
Itching can be caused by various factors such as allergic reactions, infections, or hormonal imbalances.
2. Burning sensation
Labial irritation can also cause a burning sensation.
This sensation may be localized to the labia minora or may radiate to the surrounding area.
A burning sensation can be uncomfortable and may be accompanied by redness or swelling.
3. Redness and swelling
Redness and swelling are common signs of labial irritation.
The labia minora may appear red and swollen, and the surrounding skin may also be affected.
These symptoms can be caused by infections, allergic reactions, or other irritants.
4. Dryness and flaking
Labial irritation can also result in dryness and flaking of the skin.
The labia minora may feel dry to the touch and may appear flaky or peeling.
Dryness and flaking can be caused by hormonal imbalances, fungal infections, or poor hygiene.
5. Pain or discomfort
Pain or discomfort in the labial area is another symptom of irritation.
This can range from mild to severe and may be aggravated by activities such as walking, sitting, or sexual intercourse.
Pain or discomfort can be caused by infections, friction, or other underlying conditions.
6. Abnormal vaginal discharge
Irritation of the labia minora can sometimes be accompanied by abnormal vaginal discharge.
The discharge may be thick, clumpy, foul-smelling, or have an unusual color.
This may indicate an underlying infection or other medical condition that requires attention.
7. Painful urination
Labial irritation can cause pain or discomfort during urination.
This can be a result of inflammation or infection in the vaginal area.
If you experience painful urination along with other symptoms of irritation, it is advisable to seek medical attention.
8. Painful intercourse
Labial irritation can make sexual intercourse painful or uncomfortable.
The friction and pressure during intercourse can irritate the already sensitive labia minora, leading to pain or discomfort.
Using lubrication and practicing gentler sexual activities may help alleviate this symptom.
9. Soreness
Soreness in the labial area is a common symptom of irritation.
The labia minora may feel tender to the touch and may be sensitive to pressure.
Soreness can be caused by various factors, including infections, friction, or hormonal imbalances.
10. Tenderness
Tenderness is another symptom associated with labial irritation.
The labia minora may feel sensitive and tender, even without direct pressure or touch.
Tenderness can be accompanied by other symptoms such as redness or swelling.
Prevention and Self-Care
1. Wear breathable underwear
2. Avoid using products with irritants
3. Practice good hygiene
4. Avoid tight clothing
5. Use lubrication during intercourse
6. Keep the genital area dry
7. Avoid excessive washing and douching
8. Avoid irritants in laundry detergents
9. Stay hydrated
10. Manage stress levels
1. Wear breathable underwear
One way to prevent labial irritation is to wear breathable underwear.
Choose underwear made from natural, breathable fabrics like cotton.
Avoid synthetic materials that can trap moisture and promote bacterial or fungal growth.
Changing out of wet or sweaty underwear promptly can also help prevent irritation.
2. Avoid using products with irritants
To prevent irritants from causing labial irritation, avoid using products that contain potential irritants.
This includes scented soaps, perfumes, vaginal sprays, or douches.
Opt for gentle, fragrance-free products specifically formulated for sensitive skin.
Read labels carefully and choose products that are hypoallergenic and free from harsh chemicals.

3. Practice good hygiene
Maintaining good hygiene is essential for preventing labial irritation.
Gently clean the genital area with mild, fragrance-free soaps or simply warm water.
Avoid harsh scrubbing or excessive douching, as these can disrupt the natural balance of the vaginal area.
After using the restroom, remember to wipe from front to back to avoid spreading bacteria from the rectal area to the vaginal area.

4. Avoid tight clothing
Wearing tight clothing can contribute to labial irritation by trapping moisture and heat, creating an environment that promotes bacterial or fungal growth.
Opt for loose-fitting, breathable clothing, especially in the genital area.
Choose underwear and pants that allow for airflow and moisture-wicking properties.
5. Use lubrication during intercourse
Using lubrication during sexual intercourse can help reduce friction and minimize irritation of the labia minora.
Choose water-based or silicone-based lubricants that are specifically formulated for intimate use.
Avoid oil-based lubricants, as these can damage latex condoms and increase the risk of infections.
6. Keep the genital area dry
Keeping the genital area dry is important for preventing labial irritation.
After bathing or swimming, gently pat the area dry with a clean towel.
Avoid leaving the area damp or wearing wet underwear, as this can create a moist environment that promotes bacterial or fungal growth.
7. Avoid excessive washing and douching
While it is important to maintain good hygiene, excessive washing or douching can disrupt the natural balance of the vaginal area and lead to irritation.
Limit washing the genital area to once or twice a day and use gentle, pH-balanced cleansers.
Avoid using harsh soaps or scrubbing vigorously.
8. Avoid irritants in laundry detergents
Laundry detergents that contain irritants or fragrances can cause irritation to the labia minora.
Opt for hypoallergenic, fragrance-free laundry detergents when washing underwear or clothing that comes into contact with the genital area.
9. Stay hydrated
Drinking an adequate amount of water daily can help maintain the overall health of your body, including the genital area.
Staying hydrated promotes healthy bodily functions and can prevent dryness and dehydration that may contribute to labial irritation.
10. Manage stress levels
Stress can have an impact on various aspects of our health, including the vaginal area.
High levels of stress can disrupt hormone levels and weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections and irritations.
Practice stress-management techniques such as exercise, meditation, or engaging in hobbies to help reduce stress and promote overall well-being.

Home Remedies
1. Applying a cold compress
2. Using mild, fragrance-free soaps
3. Using plain yogurt
4. Applying aloe vera gel
5. Avoiding irritating products
6. Take warm baths with Epsom salt
7. Using over-the-counter anti-itch creams
8. Avoiding scratching or picking at the irritated area
9. Using natural oils, such as coconut or tea tree oil
10. Avoiding hot baths or showers
1. Applying a cold compress
To temporarily soothe labial irritation and reduce inflammation, apply a cold compress to the affected area.
Wrap a clean, soft cloth or ice pack in a thin towel and place it gently on the labia minora for a few minutes.
The cold temperature can help numb the area and alleviate discomfort.
2. Using mild, fragrance-free soaps
When cleaning the genital area, opt for mild, fragrance-free soaps or cleansers specifically formulated for sensitive skin.
Harsh soaps or cleansers can strip away the natural oils and disrupt the pH balance of the vaginal area, leading to irritation.
Gently wash the area with lukewarm water and a gentle cleanser, and remember to rinse thoroughly.
3. Using plain yogurt
Plain, unsweetened yogurt can provide relief for labial irritation caused by fungal infections.
Yogurt contains beneficial bacteria, such as lactobacillus acidophilus, which can help restore the natural balance of the vaginal flora.
Apply a thin layer of plain yogurt to the labia minora and leave it on for a few minutes before rinsing off with lukewarm water.
4. Applying aloe vera gel
Aloe vera gel has soothing and anti-inflammatory properties that can help alleviate labial irritation.
Apply a small amount of pure aloe vera gel to the affected area and gently massage it in.
Leave the gel on for a few minutes and rinse off with lukewarm water.
Repeat this a few times a day as needed.
5. Avoiding irritating products
To prevent further irritation, avoid using products that contain potential irritants.
This includes scented toilet paper, wipes, or feminine hygiene sprays.
Opt for unscented, hypoallergenic products that are specifically designed for sensitive skin.
6. Take warm baths with Epsom salt
Taking warm baths with Epsom salt can help relieve labial irritation and soothe discomfort.
Dissolve a small amount of Epsom salt in warm water and soak it in the bath for about 15-20 minutes.
Warm water and Epsom salt can help reduce inflammation and promote relaxation.
7. Using over-the-counter anti-itch creams
Over-the-counter anti-itch creams or ointments can provide temporary relief from labial irritation.
These products typically contain ingredients like hydrocortisone or calamine, which can help reduce itching and inflammation.
Follow the instructions on the packaging and use as directed.
8. Avoiding scratching or picking at the irritated area
While it may be tempting to scratch or pick at the irritated area, this can worsen symptoms and increase the risk of infection.
Scratching can cause further damage to the delicate skin of the labia minora and introduce harmful bacteria.
If you feel the urge to scratch, try using a cold compress or applying an anti-itch cream instead.
9. Using natural oils, such as coconut or tea tree oil
Natural oils, such as coconut oil or tea tree oil, can provide relief for labial irritation.
These oils have moisturizing and antimicrobial properties that can soothe the skin and help prevent infections.
Apply a small amount of oil to the affected area and gently massage it in.
Use pure, high-quality oils and discontinue use if any irritation occurs.
10. Avoiding hot baths or showers
Hot baths or showers can worsen labial irritation by further drying out the skin.
Opt for lukewarm water instead, as hot water can strip away the natural oils and disrupt the balance of the vaginal area.
Limit the duration of baths or showers to prevent excessive moisture loss.

Medical Treatments
1. Antifungal creams or medications
2. Topical corticosteroids
3. Antibiotics for bacterial infections
4. Antiviral medications for viral infections
5. Hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms
6. Surgery for certain conditions
7. Cryotherapy for certain conditions
8. Laser therapy for certain conditions
9. Biopsy for further evaluation
10. Prescription-strength creams or ointments
1. Antifungal creams or medications
If labial irritation is caused by a fungal infection, antifungal creams or medications may be prescribed by a healthcare professional.
These treatments are designed to target and eliminate fungal overgrowth, reducing symptoms such as itching or discomfort.
It is important to follow the instructions provided and complete the full course of treatment to ensure the infection is fully treated.
2. Topical corticosteroids
For severe or persistent labial irritation, topical corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
These medications can help relieve itching, redness, and swelling.
However, prolonged use of corticosteroids should be done under medical supervision, as they can have side effects.
3. Antibiotics for bacterial infections
If labial irritation is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be necessary to clear the infection.
A healthcare professional will determine the appropriate antibiotic based on the specific bacteria causing the infection.
It is important to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed to ensure effective treatment.
4. Antiviral medications for viral infections
In cases where labial irritation is caused by a viral infection, such as herpes, antiviral medications may be prescribed by a healthcare professional.
These medications can help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms.
It is important to discuss the potential benefits and risks of antiviral medications with a healthcare professional.
5. Hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms
If labial irritation is a result of hormonal imbalances associated with menopause, hormone therapy may be recommended to alleviate symptoms.
Estrogen therapy can help restore moisture and elasticity to the vaginal tissues, reducing dryness and irritation.
Hormone therapy should be discussed with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable approach and potential risks.
6. Surgery for certain conditions
In some cases, surgical intervention may be required to treat underlying conditions that cause labial irritation.
This may include procedures to correct structural abnormalities, remove cysts or growths, or repair damaged tissue.
The specific surgical approach will depend on the individual’s condition and the recommendation of a healthcare professional.
7. Cryotherapy for certain conditions
Cryotherapy, which involves freezing tissue to destroy abnormal cells, may be used to treat certain conditions that cause labial irritation.
This procedure can be used to remove genital warts caused by HPV or to treat precancerous or cancerous lesions.
Cryotherapy is typically performed by a healthcare professional and may require multiple sessions.
8. Laser therapy for certain conditions
Laser therapy is another treatment option for certain conditions that cause labial irritation.
This procedure uses targeted laser energy to remove abnormal cells or promote tissue regeneration.
Laser therapy may be used to treat conditions such as vaginal atrophy, scar tissue, or excessive pigmentation.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the suitability and potential benefits of laser therapy.
9. Biopsy for further evaluation
In cases where the cause of labial irritation is unclear or if there are concerns about underlying conditions, a biopsy may be recommended.
A biopsy involves the removal of a small tissue sample for further evaluation under a microscope.
This can help identify any abnormal cells or determine the presence of certain conditions.
A healthcare professional will determine if a biopsy is necessary and perform the procedure if needed.
10. Prescription-strength creams or ointments
In more severe or persistent cases of labial irritation, prescription-strength creams or ointments may be recommended by a healthcare professional.
These medications may contain stronger or specialized ingredients to address specific underlying causes.
It is important to follow the instructions provided by the healthcare professional and discuss any concerns or side effects.

When to See a Doctor
1. Persistent or worsening symptoms
2. Severe pain or discomfort
3. Bleeding or unusual discharge
4. Fever or signs of infection
5. Rash or blisters
6. Sores or ulcers
7. Swollen lymph nodes in the groin area
8. Symptoms that interfere with daily activities
9. Recurrent or chronic irritation
10. Concerns about a potential STI
1. Persistent or worsening symptoms
If labial irritation persists or worsens despite home remedies and self-care measures, it is important to seek medical attention.
Persistent or worsening symptoms may indicate an underlying condition that requires further evaluation and treatment.
2. Severe pain or discomfort
Severe pain or discomfort associated with labial irritation should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
This may indicate a more significant underlying issue that requires medical intervention.
3. Bleeding or unusual discharge
If you experience bleeding or unusual discharge along with labial irritation, it is important to see a doctor.
This may indicate an infection or other medical condition that requires attention.
4. Fever or signs of infection
Fever or signs of infection, such as chills, increased body temperature, or flu-like symptoms, along with labial irritation should prompt a visit to a healthcare professional.
These symptoms may indicate a more serious infection that requires treatment.
5. Rash or blisters
The presence of a rash or blisters in the genital area along with labial irritation should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
These symptoms may be indicative of a specific condition, such as herpes, and require proper diagnosis and treatment.
6. Sores or ulcers
If labial irritation is accompanied by the development of sores or ulcers, it is important to seek medical evaluation.
These symptoms may be indicative of a sexually transmitted infection or other more serious condition.
7. Swollen lymph nodes in the groin area
Swollen lymph nodes in the groin area along with labial irritation may be a sign of an underlying infection or inflammatory process.
It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
8. Symptoms that interfere with daily activities
If labial irritation is significantly impacting your daily activities, such as walking, sitting, or sexual intercourse, it is important to seek medical attention.
Chronic or severe irritation can have a significant impact on quality of life and may require medical intervention.
9. Recurrent or chronic irritation
If labial irritation is recurrent or chronic, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional.
Chronic irritation may be indicative of an underlying condition that requires ongoing management or treatment.
10. Concerns about a potential STI
If you have concerns about a potential sexually transmitted infection (STI), it is advisable to seek medical evaluation.
A healthcare professional can provide testing, diagnosis, and appropriate treatment.
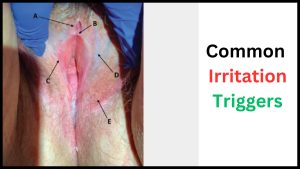
Common Irritation Triggers
1. Certain fabrics
2. Harsh soaps or detergents
3. Chemical additives in personal care products
4. Spermicides or contraceptive methods
5. Dry or cold weather
6. Menstruation or hormonal changes
7. Frequent or vigorous sexual activity
8. Certain medications
9. Excessive washing or douching
10. Weakened immune system
1. Certain fabrics
Some fabrics, such as synthetic materials or those with rough textures, can irritate the delicate skin of the labia minora.
Opt for underwear and clothing made from natural, breathable fabrics like cotton.
2. Harsh soaps or detergents
Harsh soaps or detergents can strip away the natural oils and disrupt the pH balance of the vaginal area, leading to irritation.
Choose mild, fragrance-free cleansers and laundry detergents that are gentle on sensitive skin.
3. Chemical additives in personal care products
Certain personal care products, such as scented soaps, perfumes, or vaginal sprays, can contain chemical additives that may irritate the labia minora.
Read product labels and choose fragrance-free, hypoallergenic options.
4. Spermicides or contraceptive methods
Some spermicides or certain types of contraception, such as condoms or diaphragms, can cause irritation in the genital area.
If you experience irritation after using certain products, consider switching to alternative options or discussing with a healthcare professional.
5. Dry or cold weather
Dry or cold weather can contribute to labial dryness and irritation.
Use protective clothing and consider using moisturizers specifically formulated for sensitive skin to prevent dryness.
6. Menstruation or hormonal changes
Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during menstruation or pregnancy, can lead to labial irritation.
Increased sensitivity and changes in vaginal pH can contribute to discomfort.
Maintaining good hygiene and using appropriate menstrual products can help manage symptoms.
7. Frequent or vigorous sexual activity
Frequent or vigorous sexual activity can cause friction and irritation of the labia minora.
Using appropriate lubrication and practicing gentler sexual activities can help reduce irritation and discomfort.
8. Certain medications
Some medications may have side effects that can contribute to labial irritation.
If you suspect that a medication you are taking may be causing irritation, consult with your healthcare professional for potential alternatives or adjustments.
9. Excessive washing or douching
Excessive washing or douching can disrupt the natural balance of the vaginal area and lead to irritation.
Limit washing to once or twice a day with mild, fragrance-free cleansers.
10. Weakened immune system
A weakened immune system can make the body more susceptible to infections and irritations in the genital area.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition and stress management, can help support a strong immune system.

Complications
1. Secondary bacterial or fungal infections
2. Open sores or ulcers
3. Scarring or skin changes
4. Chronic pain or discomfort
5. Psychological distress
6. Impact on sexual relationships
7. Recurrent or chronic irritation
8. Disruption of daily activities
9. Chronic inflammation or autoimmune conditions
10. Complications during pregnancy
1. Secondary bacterial or fungal infections
Untreated or unresolved labial irritation can lead to secondary bacterial or fungal infections.
Bacteria or fungi can take advantage of the disrupted skin barrier and cause further inflammation and discomfort.
2. Open sores or ulcers
Severe or chronic labial irritation can result in the development of open sores or ulcers.
These can be painful, increase the risk of infection, and may require medical attention.
3. Scarring or skin changes
In some cases, labial irritation can lead to scarring or permanent changes in the skin.
This can result in long-term discomfort or aesthetic concerns.
4. Chronic pain or discomfort
Untreated or unresolved labial irritation can lead to chronic pain or discomfort.
This can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and mental well-being.
5. Psychological distress
Labial irritation can cause psychological distress, including anxiety, embarrassment, or low self-esteem.
It is important to seek support and communicate with a healthcare professional if experiencing psychological distress related to labial irritation.
6. Impact on sexual relationships
Labial irritation can impact sexual relationships, as it can cause pain, discomfort, or anxiety during sexual activity.
Open communication with your partner and seeking medical treatment can help address this issue.
7. Recurrent or chronic irritation
If labial irritation is recurrent or chronic, it may require ongoing management or treatment.
This can have a significant impact on an individual’s daily life and may require the support of a healthcare professional.
8. Disruption of daily activities
Severe or chronic labial irritation can disrupt daily activities such as walking, sitting, or engaging in physical activities.
It is important to seek medical attention if irritation is interfering with normal daily functioning.
9. Chronic inflammation or autoimmune conditions
In some cases, labial irritation may be a symptom of chronic inflammation or underlying autoimmune conditions such as lichen sclerosus or vulvodynia.
Proper evaluation and management by a healthcare professional may be necessary.
10. Complications during pregnancy
Severe or unresolved labial irritation during pregnancy can increase the risk of complications, such as infections or difficulty with vaginal delivery.
It is important to seek medical attention if experiencing significant labial irritation during pregnancy.

Diagnosis and Evaluation
1. Medical history and symptoms assessment
2. Physical examination of the genital area
3. Laboratory tests, such as swab or culture tests
4. Microscopic examination of discharge or skin samples
5. Biopsy for further evaluation
6. Pelvic examination or colposcopy
7. Ultrasound or imaging tests
8. Hormonal level evaluation
9. Allergy testing
10. Sexually transmitted infection tests
1. Medical history and symptoms assessment
A healthcare professional will begin the evaluation of labial irritation by taking a detailed medical history and assessing the specific symptoms experienced.
This includes asking about the onset, duration, and severity of symptoms, as well as any associated factors or triggers.
2. Physical examination of the genital area
A physical examination of the genital area will be conducted by a healthcare professional to assess the extent and characteristics of the labial irritation.
This may include visual inspection and palpation of the labia minora and surrounding tissues.
3. Laboratory tests, such as swab or culture tests
Laboratory tests, such as swabs or culture tests, may be performed to identify the specific cause of labial irritation.
Swabs may be taken from the affected area to check for the presence of bacterial or fungal infections.
4. Microscopic examination of discharge or skin samples
Microscopic examination of discharge or skin samples may be done to evaluate the cellularity or presence of abnormal cells.
This can help diagnose certain conditions or rule out more serious underlying issues.
5. Biopsy for further evaluation
In cases where the cause of labial irritation is unclear or if there are suspicions of an underlying condition, a biopsy may be recommended.
A small tissue sample may be taken and examined under a microscope to assess for abnormal cell growth or underlying disorders.
6. Pelvic examination or colposcopy
In some cases, a pelvic examination or colposcopy may be performed to evaluate the overall health of the genital area, including the cervix, vagina, and labia minora.
This can help identify any abnormalities or additional factors contributing to the labial irritation.
7. Ultrasound or imaging tests
In certain situations, ultrasound or other imaging tests may be ordered to evaluate the pelvic region or rule out underlying structural abnormalities or conditions causing labial irritation.
8. Hormonal level evaluation
If hormonal imbalances are suspected as a cause of labial irritation, hormone level evaluation may be performed.
This can include blood tests to assess hormone levels and identify any abnormalities.
9. Allergy testing
If an allergic reaction is suspected as the cause of labial irritation, allergy testing may be recommended.
This can help identify specific allergens and guide future avoidance or management strategies.
10. Sexually transmitted infection tests
If there is concern about a sexually transmitted infection (STI) as the cause of labial irritation, specific tests for STIs may be ordered.
These can include blood tests, urine tests, or swabs of the affected area.
Conclusion:
Labial irritation can be caused by various factors, including allergic reactions, infections, poor hygiene, or hormonal imbalances.
Symptoms of irritation may include itching, burning, redness, swelling, or discomfort.
Preventive measures such as wearing breathable underwear, avoiding irritants, practicing good hygiene, and using lubrication during intercourse can help reduce the risk of irritation.
Home remedies such as applying a cold compress, using mild soaps, or avoiding scratching can provide temporary relief.
However, if symptoms persist or worsen, medical evaluation and treatment may be necessary.
Physicians may prescribe antifungal or antibacterial medications, topical corticosteroids, or provide hormonal therapy to address underlying causes of labial irritation.
It is important to seek medical attention for persistent or severe symptoms, as well as any concerns about sexually transmitted infections.
With proper care and management, labial irritation can be effectively treated, reducing discomfort and improving overall well-being.









